Pradaxa: An Effective Anticoagulant with a Spectrum of Indications
In the realm of cardiovascular medicine, blood thinners play a crucial role in preventing the formation of blood clots, which can lead to potentially life-threatening events such as strokes and heart attacks. Among the various blood thinners available, Pradaxa, also known as dabigatran etexilate mesylate, stands out as a widely prescribed medication for a range of conditions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Pradaxa, exploring its mechanisms of action, therapeutic applications, potential side effects, and essential precautions.
Understanding What is Pradaxa: A Closer Look
Pradaxa, an oral anticoagulant, belongs to a class of medications known as direct thrombin inhibitors. These drugs directly target thrombin, an enzyme that plays a critical role in the blood clotting process. By blocking thrombin’s activity, Pradaxa effectively prevents blood clots from forming.
Pradaxa Generic: An Affordable Alternative
In line with the growing emphasis on cost-effective healthcare, generic dabigatran etexilate mesylate capsules emerged as a viable alternative to the brand-name Pradaxa. These generic formulations undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the same stringent standards of safety and efficacy as their brand-name counterparts. The availability of generic Pradaxa has expanded access to this crucial medication, making it more affordable for patients who require anticoagulation therapy.
What is the Drug Pradaxa Used for: A Spectrum of Indications
Pradaxa, an oral anticoagulant medication, has become a cornerstone of treatment for a variety of cardiovascular conditions, particularly those involving blood clot formation. Its efficacy and favorable safety profile have made it a preferred choice for many patients and healthcare providers. Here, we delve into the diverse therapeutic applications of Pradaxa, exploring its role in preventing and managing various conditions.
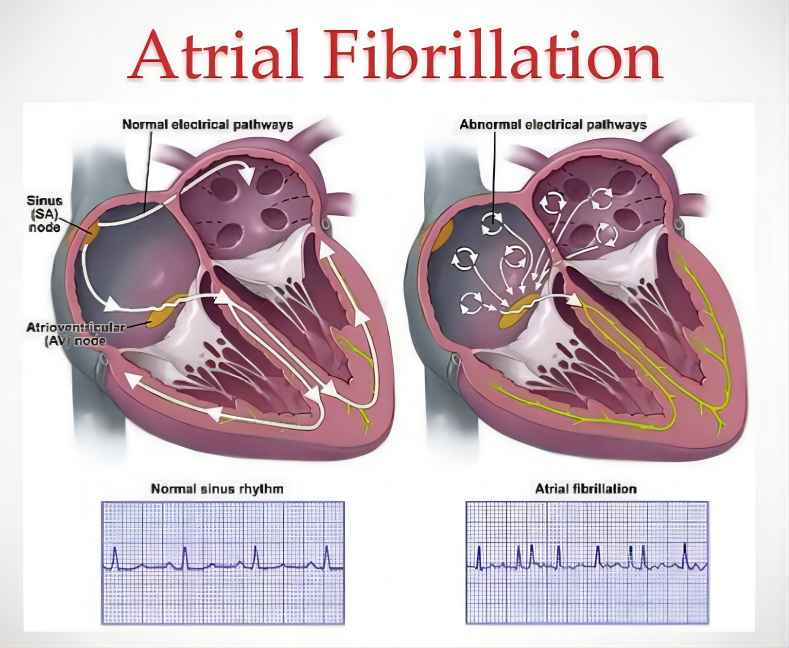
1. Prevention of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
AFib, a common heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and often rapid heartbeats, poses a significant risk of stroke due to the increased likelihood of blood clots forming in the heart. These clots can dislodge and travel through the bloodstream, potentially causing strokes or blockages in other organs. Pradaxa has emerged as a frontrunner in preventing stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular AFib. Clinical trials, including the RE-DUCE-AF study, have demonstrated Pradaxa’s non-inferiority to warfarin, a long-established anticoagulant, in preventing stroke and systemic embolism. Moreover, Pradaxa has been shown to cause a significantly lower risk of major bleeding events compared to warfarin, making it a safer option for many patients.
2. Treatment of Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
DVT and PE are serious conditions characterized by blood clots forming in deep veins and the lungs, respectively. These clots can lead to a range of complications, including reduced blood flow, tissue damage, and even death. Pradaxa has proven effective in treating acute DVT and PE, helping to dissolve the existing clots and prevent further clot formation. Its efficacy has been demonstrated in clinical trials, such as the REWARD-DVT and EINSTEIN-PE studies, which showed that Pradaxa was non-inferior to warfarin in treating DVT and PE, while also demonstrating a lower risk of major bleeding events.
3. Prevention of Recurrent Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
After an initial treatment course for acute DVT or PE, it is crucial to prevent the recurrence of these potentially life-threatening conditions. Pradaxa has established its efficacy in preventing recurrent DVT and PE, providing long-term protection against these complications. Clinical trials, including the RE-DUCE and EINSTEIN studies, have demonstrated that Pradaxa is effective in preventing recurrent DVT and PE, with a lower risk of major bleeding events compared to warfarin.
4. Pradaxa’s Versatility in Addressing Cardiovascular Concerns
Pradaxa’s therapeutic applications extend beyond the realm of AFib, DVT, and PE, making it a versatile tool for managing various cardiovascular conditions. It is also used in the treatment of chronic DVT and PE, providing long-term management options for patients with these conditions. Additionally, Pradaxa is being investigated for potential applications in other cardiovascular areas, such as the prevention of stroke in patients with a history of transient ischemic attack (TIA) and the prevention of cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease.

Pradaxa’s Mechanism of Action: Disrupting the Clotting Cascade
Pradaxa’s effectiveness in preventing blood clots hinges on its ability to directly inhibit thrombin, a crucial enzyme in the blood clotting cascade. This cascade, a series of complex reactions, is responsible for the formation of blood clots at the site of vessel injury, preventing excessive blood loss. However, in certain conditions, such as AFib, DVT, and PE, the clotting cascade can become overactive, leading to the formation of unwanted blood clots in the bloodstream. This is where Pradaxa steps in, specifically targeting thrombin to disrupt this excessive clotting process.
1. Thrombin: The Maestro of Coagulation
Thrombin, a serine protease enzyme, plays a pivotal role in the blood clotting cascade. It acts as a maestro, orchestrating the conversion of fibrinogen, a soluble plasma protein, into fibrin, an insoluble protein that forms the structural framework of blood clots. This fibrin polymerization is essential for stopping bleeding at the site of vessel injury.
2. Pradaxa’s Precision Targeting: Disrupting the Clotting Process
Pradaxa’s mechanism of action lies in its ability to directly and reversibly bind to the active site of thrombin, effectively blocking its catalytic activity. This targeted inhibition prevents thrombin from converting fibrinogen into fibrin, thereby disrupting the formation of blood clots. By selectively targeting thrombin, Pradaxa minimizes interference with other essential processes in the body, contributing to its favorable safety profile.
3. A Multifaceted Approach to Blood Clot Prevention
Pradaxa’s anticoagulant effect extends beyond its direct inhibition of thrombin. It also indirectly influences the clotting cascade by preventing the activation of Factor Xa, another crucial enzyme involved in fibrin polymerization. Additionally, Pradaxa inhibits the production of thrombin by interfering with the activation of antithrombin III, a natural anticoagulant protein that regulates thrombin activity.
4. A Precise Instrument in the Cardiovascular Arsenal
Pradaxa’s precise mechanism of action, targeting thrombin without disrupting other essential physiological processes, makes it a valuable tool in preventing blood clots in various cardiovascular conditions. Its ability to effectively disrupt the clotting cascade while minimizing bleeding risks has positioned Pradaxa as a preferred anticoagulant option for many patients and healthcare providers.
Side Effects and Precautions of Pradaxa: Essential Considerations
While Pradaxa offers significant benefits in preventing blood clots, it is crucial to be aware of its potential side effects and exercise caution during its use. A thorough understanding of these considerations is essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of Pradaxa in various patient populations.
Potential Side Effects: A Closer Look
Pradaxa’s most common side effects are typically mild and manageable. These include:
- Gastrointestinal disturbances: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Bleeding: Easy bruising, minor bleeding (e.g., nosebleed, bleeding from cuts)
- Skin reactions: Rashes, itching
In rare instances, more severe side effects can occur, including:
- Major bleeding: Bleeding that requires hospitalization or transfusion
- Severe allergic reactions: Anaphylaxis, angioedema
- Other complications: Liver injury, kidney injury, spinal hematoma
Precautions and Contraindications: Prioritizing Patient Safety
Pradaxa is contraindicated in certain patient populations due to an increased risk of adverse events. These include:
- Severe renal impairment: Patients with creatinine clearance < 15 mL/min
- Active bleeding: Ongoing bleeding or increased risk of bleeding
- History of hypersensitivity to Pradaxa or its components
Pradaxa should be used with caution in patients with certain medical conditions, including:
- Liver impairment: Patients with Child-Pugh C cirrhosis
- Recent epidural or spinal puncture: Increased risk of spinal hematoma
- Uncontrolled hypertension: Risk of increased bleeding
Drug Interactions: A Symphony of Medications
Pradaxa can interact with other medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. It is crucial to inform healthcare providers about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, before starting Pradaxa. Medications that may interact with Pradaxa include:
- Antiplatelet agents: Aspirin, clopidogrel, prasugrel
- Certain antidepressants: Fluoxetine, sertraline
- Antiarrhythmic drugs: Amiodarone, quinidine
Patient Education and Monitoring: A Collaborative Approach
Effective communication and monitoring are essential during Pradaxa therapy. Patients should be educated about the potential side effects, precautions, and drug interactions associated with Pradaxa. Regular monitoring of bleeding risk, renal function, and liver function is crucial for ensuring patient safety.

Conclusion: Navigating the Path to Effective Anticoagulation
Pradaxa has established itself as a valuable tool in the management of AFib and other conditions requiring anticoagulation therapy. Its effectiveness in preventing stroke and systemic embolism, coupled with its favorable safety profile compared to other anticoagulants, has made it a preferred choice for many patients and healthcare providers. As research and development in anticoagulant therapy continue, Pradaxa remains a focus of ongoing studies evaluating its potential benefits and limitations in various patient populations and clinical settings. The ongoing pursuit of improved anticoagulant therapies aims to provide patients with even more effective and safer options for preventing blood clots and associated complications.