Dacomitinib: A Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Dacomitinib is a medication used to treat a specific type of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It belongs to a class of drugs known as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). This article explores Dacomitinib, its active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), mechanism of action, uses, potential side effects, and manufacturing processes.
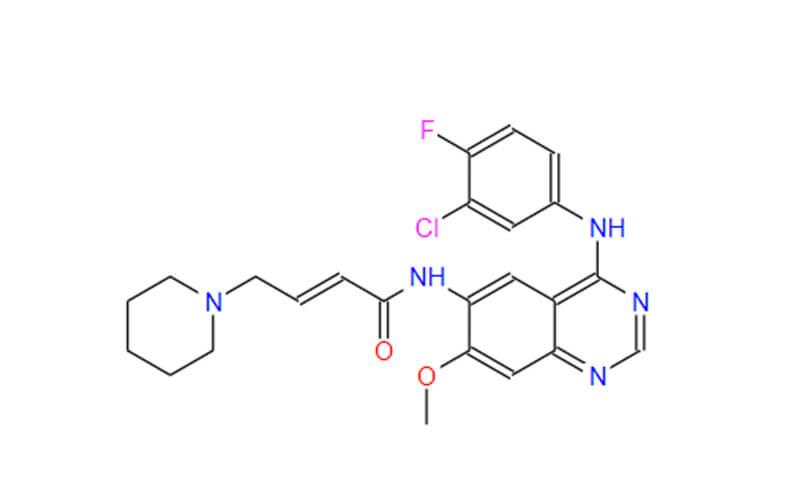
What is Dacomitinib API?
Dacomitinib’s effectiveness hinges on its active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), the specific chemical compound responsible for the drug’s therapeutic effects. The API undergoes a rigorous production process to ensure its purity, potency, and safety. Here’s a breakdown of the API’s significance:
- Essential for Drug Action: The Dacomitinib API is the centerpiece of the medication. It directly interacts with the targeted molecules in the body, producing the desired therapeutic outcome.
- Strict Manufacturing Standards: The production of Dacomitinib API adheres to stringent guidelines set by regulatory bodies like the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). These regulations ensure the API meets specific quality and safety criteria.
- Global Availability: Dacomitinib manufacturers worldwide must comply with these international standards, guaranteeing consistent quality of the API used in the final medication, regardless of location.
How Dacomitinib API is Manufactured?
Dacomitinib API undergoes a meticulous and complex manufacturing process to guarantee its quality, purity, and safety. Here’s a simplified overview of the key steps involved:
- Synthesis Route Design: Chemists meticulously design one or more synthesis routes to create the Dacomitinib molecule from readily available starting materials. Factors like cost, efficiency, environmental impact, and final product quality influence the chosen route.
- Laboratory-Scale Synthesis: Once a synthesis route is selected, scientists perform the reaction on a small scale in a laboratory setting. This allows for optimization of reaction conditions, such as temperature, time, and solvents, to ensure efficient and high-quality production.
- Scale-Up Production: After successful laboratory-scale synthesis, the process is scaled up for large-scale manufacturing. This might involve adjustments to reaction conditions and equipment to accommodate bigger production volumes.
- Purification and Separation: Once the desired molecule is synthesized, it needs to be purified from unreacted starting materials, byproducts, and impurities. Techniques like crystallization, filtration, extraction, and chromatography are employed to achieve high levels of Dacomitinib API purity.
- Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures are implemented. Raw materials, intermediate products, and the final Dacomitinib API undergo rigorous testing using sophisticated analytical techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), mass spectrometry (MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to ensure adherence to pre-defined quality specifications.
- Packaging and Storage: Qualified Dacomitinib API is then appropriately packaged and stored under controlled conditions to prevent contamination, degradation, and maintain its stability during transportation and storage until it reaches pharmaceutical companies for final drug formulation.
- Documentation: Detailed documentation of the entire manufacturing process, including batch records, quality control test results, and stability data, is maintained for traceability and regulatory compliance.
- Compliance Checks: Manufacturing facilities and processes are subject to regular inspections by regulatory bodies to ensure adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) standards. These standards guarantee the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Dacomitinib API manufacturing is a highly specialized and regulated process that demands expertise in chemistry, engineering, and quality control. Pharmaceutical companies invest significantly in sophisticated equipment, rigorous quality control procedures, and adherence to international regulations to ensure the consistent production of safe and effective Dacomitinib for patients worldwide.
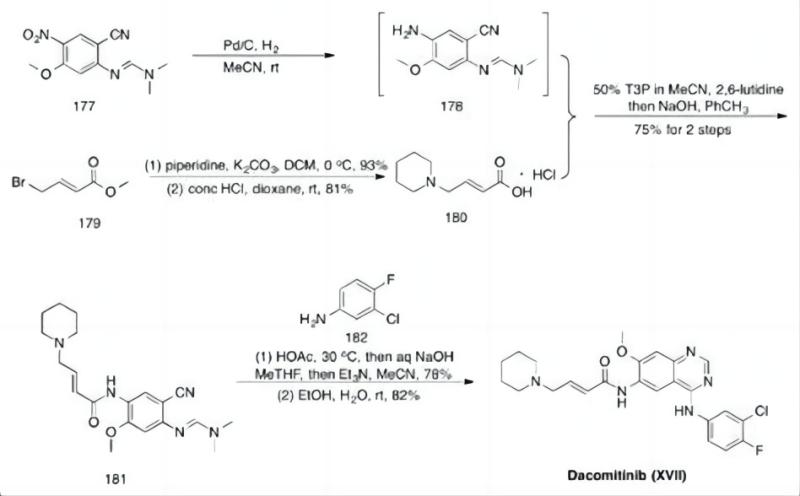
Qingmu: a Potential Dacomitinib API Manufacturer
Qingmu, with a reputation for quality API production, is a pharmaceutical manufacturer known for its expertise in Human APIs (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients for human use).
Here’s what to potentially expect from a manufacturer like Qingmu:
- Compliance with Global Standards: Adherence to cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practice) regulations ensures the API meets international quality and safety benchmarks.
- Focus on Cost-Effectiveness: Qingmu is known for offering its human APIs at competitive prices, potentially making Dacomitinib treatment more accessible to patients.
- Diverse API Portfolio: Manufacturing over 30 different human APIs suggests a robust infrastructure and expertise in handling complex API production processes.
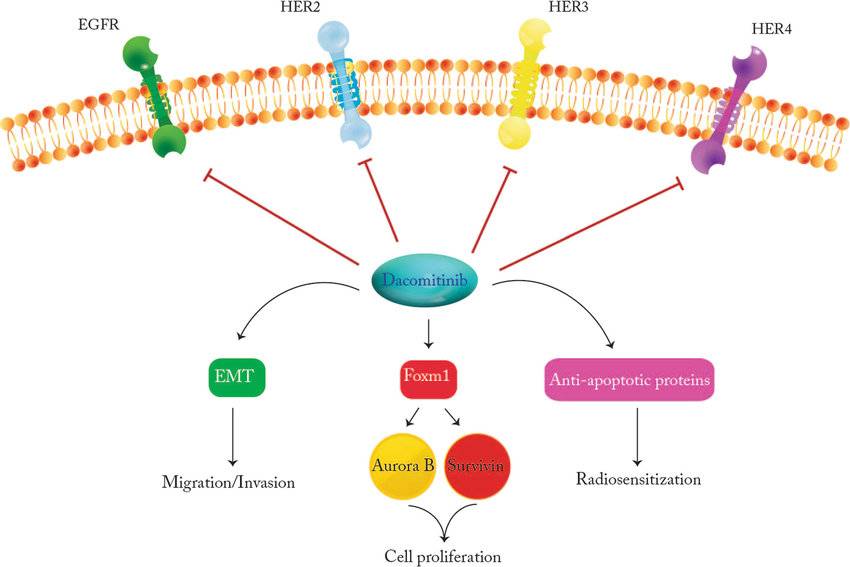
Mechanism of Action of Dacomitinib
Dacomitinib’s therapeutic efficacy stems from its targeted action on EGFR. EGFR is a protein found on the surface of cells that plays a critical role in cell growth, proliferation, and survival. In certain NSCLC cases, mutations occur in the EGFR gene, leading to its overactivation. This uncontrolled activation fuels the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Dacomitinib works by specifically targeting the EGFR protein:
- EGFR Kinase Inhibition: Dacomitinib binds to the EGFR’s kinase domain, an essential part of the protein responsible for its signaling activity. This binding competitively inhibits the EGFR from binding to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a crucial molecule for its activation.
- Disrupting Signaling Pathways: By preventing EGFR activation, Dacomitinib disrupts downstream signaling pathways critical for cancer cell growth and survival. These pathways include Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR, which regulate cell cycle progression and proliferation.
- Inducing Cell Death (Apoptosis): Disruption of these signaling pathways by Dacomitinib can trigger apoptosis, a programmed cell death process. This targeted elimination of cancer cells contributes to tumor shrinkage and helps control the disease.
- Potential Anti-Angiogenic Effect: EGFR signaling also plays a role in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels. Dacomitinib might indirectly inhibit angiogenesis by suppressing EGFR activity, potentially limiting the tumor’s blood supply and hindering its growth.
By targeting EGFR and disrupting these vital pathways, Dacomitinib offers a targeted therapeutic approach for patients with NSCLC harboring specific EGFR mutations.
Dacomitinib Uses: Tailored Treatment for Specific NSCLC
Dacomitinib is primarily indicated for the treatment of EGFR-mutated NSCLC. These mutations are identified through genetic testing, which helps determine if a patient is likely to benefit from Dacomitinib therapy. Here’s a closer look at Dacomitinib’s use case:
- Targeted Therapy: Unlike traditional chemotherapy drugs that target a broad range of cells, Dacomitinib acts on a specific molecular target (EGFR mutations) associated with cancer development. This targeted approach potentially minimizes side effects compared to conventional therapies.
- Specific Mutations: Not all EGFR mutations respond equally to Dacomitinib. Testing helps identify patients with mutations known to be susceptible to Dacomitinib’s action, ensuring a more personalized treatment approach.
- Later Stages of NSCLC: Dacomitinib is typically used to treat patients with advanced (metastatic) NSCLC that has progressed after prior treatment regimens.
It’s crucial to remember that Dacomitinib is not a one-size-fits-all solution for NSCLC. Genetic testing plays a vital role in determining if a patient is a suitable candidate for this targeted therapy.

Potential Side Effects of Dacomitinib
While Dacomitinib offers a targeted approach to NSCLC treatment, it can cause side effects. Here’s a list of some common adverse reactions associated with Dacomitinib:
- Skin Reactions: Rash, dry skin, itching, and hand-foot syndrome (inflammation of the palms and soles) are frequent occurrences.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Diarrhea and mouth sores are potential side effects that can be managed with medication and dietary adjustments.
- Loss of Appetite and Fatigue: Decreased appetite and fatigue are common, potentially impacting a patient’s quality of life. Nutritional counseling and supportive medications can help manage these issues.
- Nail Changes: Dacomitinib can cause discoloration, weakening, or separation of fingernails and toenails.
- Liver Function Abnormalities: Close monitoring of liver function is essential as Dacomitinib can elevate liver enzymes. Dose adjustments or treatment breaks might be necessary in some cases.
- Eye Problems: Dry eyes or other forms of eye discomfort can occur. Regular eye examinations are recommended during treatment.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Dacomitinib might elevate the susceptibility to infections. Maintaining good hygiene and informing healthcare providers about any signs of infection is crucial.
- High Blood Pressure: Regular blood pressure monitoring is necessary, and medication adjustments might be required to manage hypertension if it develops.
- Proteinuria: The presence of excess protein in the urine, a potential sign of kidney issues, requires monitoring and potential treatment adjustments.
The severity and frequency of these side effects can vary from person to person. Open communication with the healthcare team is essential to manage these side effects effectively and ensure optimal treatment outcomes. It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list, and patients should discuss all potential side effects with their doctor before starting Dacomitinib therapy.
Conclusion
Dacomitinib offers a targeted therapeutic approach for patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC. By specifically inhibiting EGFR activity and disrupting its downstream signaling pathways essential for cancer cell growth, Dacomitinib can help control tumor progression. Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying patients who can potentially benefit from this targeted therapy. While Dacomitinib can cause side effects, these are often manageable with proper monitoring and intervention by the healthcare team. The complex and regulated manufacturing process ensures the quality and safety of the Dacomitinib API, providing a reliable treatment option for eligible patients with NSCLC.