Dabigatran: Revolutionizing Anticoagulant Treatment
In recent years, the field of anticoagulation therapy has experienced a remarkable transformation, characterized by the emergence of innovative medications that offer enhanced effectiveness, safety, and convenience to patients. Leading this transformative shift is Dabigatran, a groundbreaking anticoagulant developed by Boehringer Ingelheim, which has garnered widespread acclaim for its pivotal role in preventing strokes, blood clots, and associated medical complications. This article explores the multifaceted realm of Dabigatran, delving into its mechanism of action, advantages compared to traditional treatments, and clinical applications.
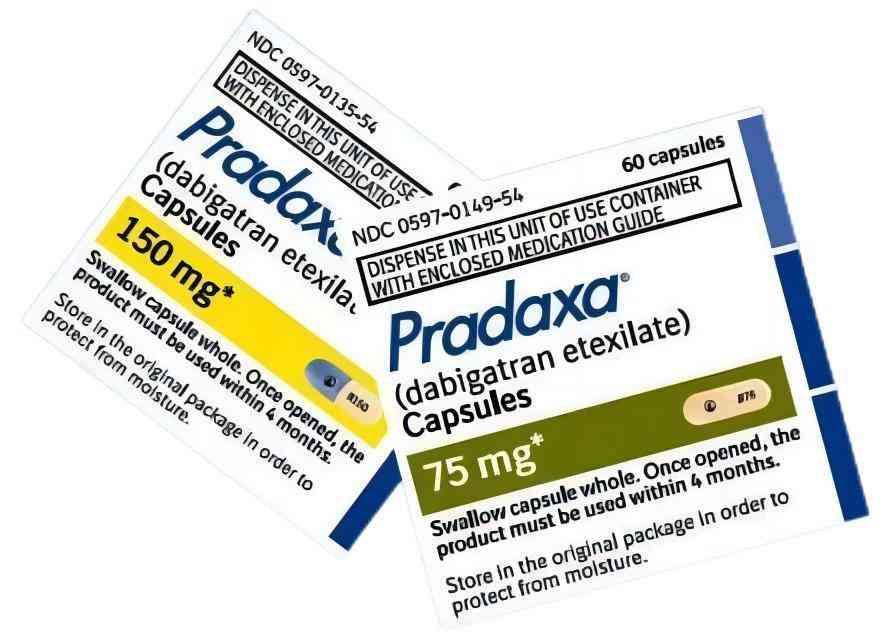
New Era of Anticoagulation
The increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases worldwide underscored the demand for innovative anticoagulation treatments. Conditions like atrial fibrillation (AFib), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism (PE) posed significant challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. Traditional anticoagulants, such as warfarin, necessitated meticulous blood level monitoring and imposed strict dietary limitations, limiting their convenience and occasionally compromising patient compliance.
However, the introduction of dabigatran marked a new era in anticoagulation therapy. Developed by Boehringer Ingelheim, this medication is a direct thrombin inhibitor that specifically targets thrombin, a pivotal enzyme in the blood clotting process. Unlike warfarin, which interferes with multiple clotting factors, dabigatran’s precise mode of action offers several benefits, including predictability in its effects, reduced risk of bleeding, oral administration, and fewer dietary restrictions.
How Dabigatran Works?
Dabigatran, the active pharmaceutical ingredient(API) in medications like Pradaxa, is a direct thrombin inhibitor. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the activity of thrombin, a critical enzyme in the blood coagulation (clotting) cascade. Here’s a detailed explanation of how dabigatran works:
- Clotting Cascade
The process of blood clotting is highly complex, characterized by a series of coordinated events referred to as the clotting cascade. This cascade encompasses a diverse array of proteins and enzymes that interact sequentially to create blood clots in response to injuries or damage to blood vessels. Thrombin plays a pivotal role at the heart of this cascade.
- Thrombin’s Role
Thrombin is an enzyme with a central role in the concluding phases of the clotting cascade. Among its primary functions is the conversion of soluble fibrinogen, a protein found in the bloodstream, into insoluble fibrin strands. These fibrin strands intertwine, forming a meshwork that captures blood cells and establishes the structural framework of a blood clot.
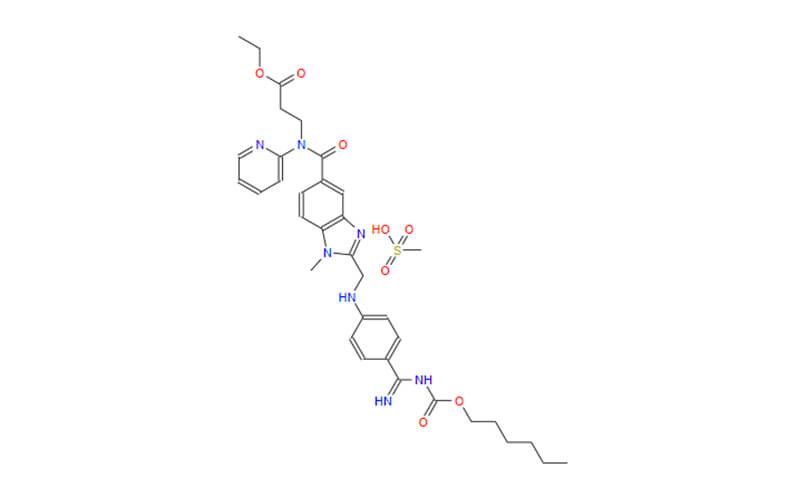
- Direct Thrombin Inhibition
Dabigatran is classified as a direct thrombin inhibitor, signifying that it directly hinders the functioning of thrombin. This is accomplished through its precise binding to thrombin, which in turn prevents thrombin from executing its enzymatic functions.
- Preventing Fibrin Formation
Through its inhibition of thrombin, dabigatran obstructs the transformation of fibrinogen into fibrin. The absence of fibrin strand formation results in impaired blood clotting. This decrease in clotting activity is instrumental in averting the creation of undesired blood clots.
- Anticoagulant Effect
Dabigatran’s interference with thrombin leads to a comprehensive anticoagulant effect, which is beneficial in a range of medical conditions characterized by the potential for excessive blood clotting. These conditions include atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and various other thromboembolic disorders.
- Predictable Dosing
Dabigatran is recognized for its consistent dosing, allowing patients to generally adhere to a stable dosage without the necessity for frequent monitoring of blood clotting indicators, like the international normalized ratio (INR), which is often essential when using warfarin. This predictability streamlines the administration of anticoagulation therapy.
- Reduced Bleeding Risk
In certain clinical situations, Dabigatran has been linked to a reduced risk of specific types of bleeding, especially intracranial bleeding (bleeding within the brain), when compared to older anticoagulants such as warfarin.
Advantages of Dabigatran Over Traditional Therapies
The introduction of dabigatran has brought several advantages to patients and healthcare providers, making it an attractive choice for anticoagulation therapy:
- Predictable Anticoagulant Effect: Dabigatran’s mechanism of action results in a more predictable and stable anticoagulant effect. Unlike warfarin, which requires frequent INR monitoring and dosage adjustments, dabigatran simplifies the management of anticoagulation therapy.
- Reduced Bleeding Risk: While all anticoagulants carry some bleeding risk, dabigatran has demonstrated a favorable safety profile compared to older agents. Extensive clinical trials conducted by the dabigatran manufacturer established its safety credentials, making it a safer choice for many patients.
- Oral Administration: Dabigatran is available in oral form, eliminating the need for injections, which are common with some other anticoagulants. This convenience enhances patient adherence to therapy.
- Fewer Dietary Restrictions: Unlike warfarin, which necessitates strict dietary restrictions, dabigatran users can enjoy a more varied diet without compromising its effectiveness. This flexibility greatly improves patients’ quality of life.
- Broad Indications: Dabigatran is approved for various indications, covering a wide spectrum of cardiovascular conditions. Its versatility ensures that it meets the needs of a diverse patient population.
Clinical Applications of Dabigatran
Dabigatran’s adaptability has broadened its scope in clinical applications, establishing it as an indispensable tool in the management of various cardiovascular conditions:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AF): Atrial fibrillation, a prevalent heart rhythm disorder, heightens the risk of stroke due to the pooling of blood in the atria. Dabigatran assumes a pivotal role in the management of AF by effectively preventing the formation of blood clots in the atria, thus reducing the risk of embolic strokes.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): DVT occurs when blood clots develop in deep veins, frequently in the legs. Dabigatran serves as a valuable therapeutic choice for both treating existing DVT and preventing the recurrence of such episodes.
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): PE is a potentially life-threatening condition resulting from dislodged blood clots that obstruct pulmonary arteries. Dabigatran is employed to thwart further clot formation and diminish the likelihood of recurrent PEs.
- Thromboprophylaxis Following Joint Replacement Surgery: Orthopedic procedures, like hip or knee replacements, come with an elevated risk of DVT. Dabigatran is employed for post-operative thromboprophylaxis, providing protective measures for patients during the critical post-surgery period.
Conclusion
Dabigatran has ushered in a remarkable transformation in the field of anticoagulation therapy. Its precision in targeting thrombin, predictable anticoagulant effect, reduced bleeding risk, oral administration, and broad clinical applications have positioned it as a frontline player in the fight against cardiovascular diseases.
As research and development initiatives continue to expand the horizons of this groundbreaking medication, Dabigatran represents a testament to the power of innovation in healthcare. With its promise of improved therapies and a brighter future for patients at risk of thrombotic events, Dabigatran stands as a beacon of hope in the ever-evolving landscape of cardiovascular medicine.
Qingmu Pharmaceutical is a China Dabigatran manufacturer that stands as a vanguard in the field of pharmaceuticals. It is committed to providing customers with high-quality products, and competitive prices.