Dabigatran Etexilate: Redefining Anticoagulant Therapy
In the realm of anticoagulant therapy, the development of novel agents has revolutionized the management of various thrombotic disorders. Among these, dabigatran etexilate stands out as a significant milestone, offering a promising alternative to traditional anticoagulants like warfarin. With its unique mechanism of action and formulation, dabigatran etexilate has garnered attention for its efficacy, safety, and convenience in clinical practice.
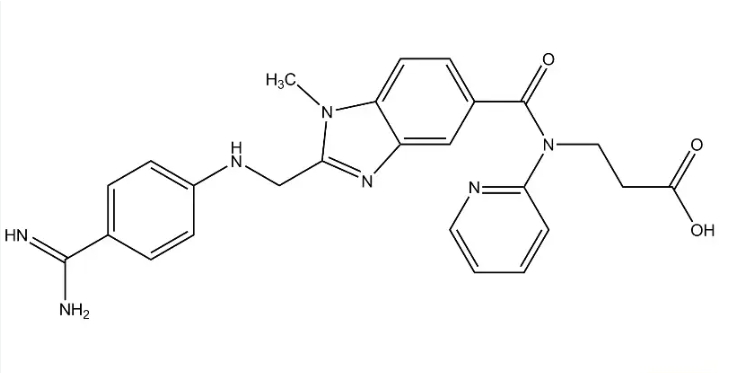
What is Dabigatran Etexilate?
Dabigatran etexilate is a medication classified as a direct thrombin inhibitor. This means it specifically targets a protein in the blood called thrombin, which plays a crucial role in clot formation. Dabigatran etexilate works by inactivating both free-floating thrombin and thrombin that’s already bound to clots. This effectively disrupts the clotting process and helps prevent new blood clots from forming.
Here’s what makes dabigatran etexilate unique compared to some other blood thinners:
- No routine monitoring: Unlike warfarin, a widely used blood thinner, dabigatran etexilate doesn’t require frequent blood tests to check its effectiveness. This eliminates the need for constant dose adjustments and simplifies treatment management for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Fixed-dose administration: Dabigatran etexilate comes in a set dose, removing the need for frequent adjustments based on individual test results. This fixed-dosing approach improves medication adherence, especially for long-term treatment plans.
- Benefits in long-term treatment: Due to its characteristics, dabigatran etexilate is particularly advantageous for conditions that require long-term blood clot prevention, such as atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat) and venous thromboembolism (blood clots in the legs or lungs).
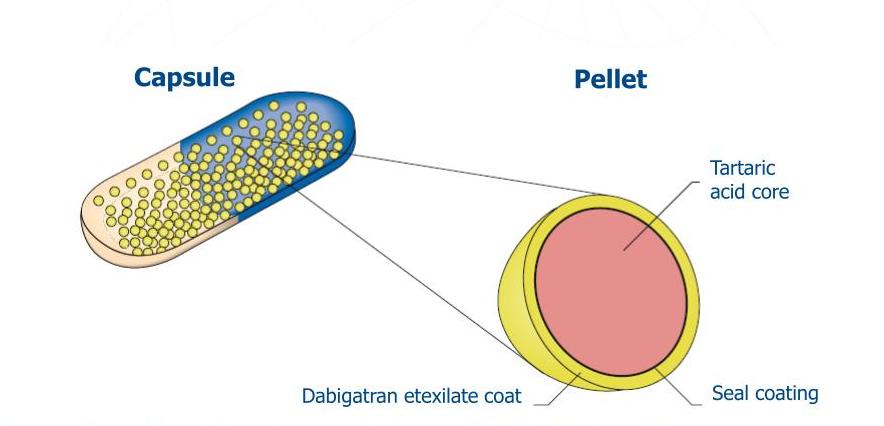
Forms of Dabigatran Etexilate
Dabigatran etexilate comes in two primary forms: capsules and pellets. While both deliver the same medication, they offer distinct advantages depending on individual needs and preferences.
Capsules: This is the more traditional form of dabigatran etexilate. Capsules come in pre-measured doses, offering simplicity and ease of use. They are a suitable option for most patients who can swallow pills without difficulty.
Pellets: These tiny spheres represent a more innovative approach. They can be formulated into capsules containing multiple pellets, allowing for greater flexibility in dosing. This is particularly beneficial for patients who require adjustments based on factors like weight, kidney function, or other medications. Additionally, dabigatran pellets offer a unique advantage for patients with swallowing difficulties. The pellets can be conveniently sprinkled onto soft food, making medication administration easier and more comfortable.

How Dabigatran Pellets are Transforming Blood Clot Prevention?
Dabigatran etexilate has emerged as a valuable tool for preventing blood clots. However, traditional tablet formulations can sometimes present challenges. Here’s where dabigatran etexilate pellets come in, offering a revolutionary approach to blood clot prevention:
- Enhanced Drug Delivery: Unlike traditional tablets, dabigatran pellets, also known as microspheres, break down into tiny particles within the digestive system. This allows for a more uniform distribution of the medication throughout the gastrointestinal tract. This even distribution significantly improves how well the body absorbs the drug (bioavailability). Consistent absorption translates into steadier levels of dabigatran etexilate in the bloodstream, reducing the risk of ineffective treatment due to under-dosing or potential complications from over-dosing.
- Flexible Dosing Options: Traditional tablets come in fixed doses. Dabigatran pellets, however, offer greater flexibility. They can be formulated into capsules containing multiple pellets, allowing for customized dosing regimens. This is particularly beneficial for patients who may require adjustments based on factors like weight, kidney function, or other medications they are taking. Moreover, for patients who have difficulty swallowing pills, these pellets can be conveniently sprinkled onto soft food, making medication administration easier.
- Improved Patient Experience: The development of dabigatran etexilate pellets represents a significant advancement in blood clot prevention therapy. By optimizing drug delivery, these pellets offer several advantages for patients:
- Reduced Side Effects: Traditional blood thinners can sometimes cause stomach upset. The more consistent drug levels achieved with dabigatran pellets have the potential to lessen these gastrointestinal side effects, leading to better tolerability and potentially improved medication adherence.
- Simplified Dosing: Dabigatran pellets are typically formulated for once-daily administration. This streamlined approach simplifies medication management and reduces the burden of remembering to take multiple doses throughout the day. This can significantly improve medication adherence, especially for patients who struggle with complex medication schedules.
- Tailored Treatment: With the flexibility of pellet formulations, healthcare providers can create customized treatment plans that cater to individual patient needs and preferences. This personalized approach can lead to better treatment outcomes.
In essence, dabigatran etexilate pellets represent a significant leap forward in oral blood clot prevention therapy. They offer enhanced drug delivery, improved patient experience, and the potential for tailored treatment plans, ultimately leading to better clinical outcomes.
Dabigatran Etexilate Across Medical Conditions
Clinical research has extensively evaluated dabigatran etexilate’s effectiveness in various situations, solidifying its role in blood clot prevention and treatment. Here’s a closer look at its efficacy across key indications:
- Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Prevention: The RE-LY trial, a landmark study, established dabigatran etexilate’s efficacy. It demonstrated that dabigatran was equally effective as warfarin (a well-established blood thinner) in preventing stroke or systemic embolism (blood clots blocking blood flow) in patients with atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat). Notably, dabigatran offered a significant advantage – a lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage (bleeding in the brain) compared to warfarin. Subsequent real-world studies have confirmed these findings, showcasing dabigatran etexilate’s consistent performance in everyday clinical practice.
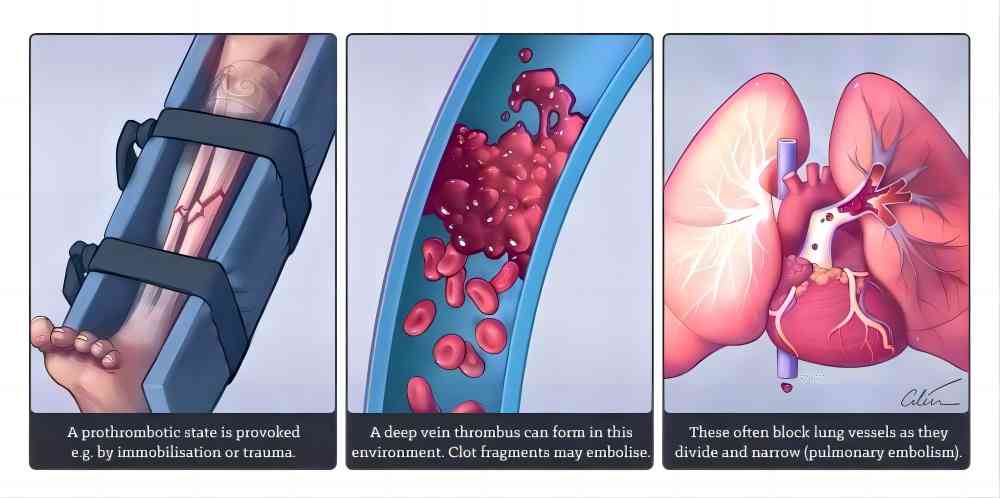
- Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention and Treatment: Dabigatran etexilate’s effectiveness extends beyond atrial fibrillation. Studies have shown its efficacy in both preventing and treating VTE, which encompasses deep vein thrombosis (DVT, blood clots in the legs) and pulmonary embolism (PE, blood clots traveling to the lungs). Compared to conventional therapy, dabigatran etexilate significantly reduces the risk of recurrent VTE events.
- Acute Management of Thromboembolic Events: Dabigatran etexilate’s rapid onset of action makes it a valuable option for the immediate management of DVT and PE. This means the medication starts working quickly to prevent further clot formation. Additionally, its predictable pharmacokinetics (how the body absorbs and eliminates the drug) allows for easier monitoring and dose adjustments if needed.
Clinical trials and real-world experience have consistently demonstrated dabigatran etexilate’s effectiveness across various blood clot-related conditions. It offers a valuable alternative to traditional blood thinners, particularly for patients at risk of stroke due to atrial fibrillation or those requiring VTE prevention or treatment.
Safety Considerations
Safety remains a paramount consideration in anticoagulant therapy, and dabigatran etexilate has demonstrated a favorable safety profile overall. While bleeding is a recognized adverse effect of anticoagulants, dabigatran etexilate has shown comparable or lower rates of major bleeding compared to warfarin in clinical trials. Furthermore, the absence of routine monitoring requirements reduces the burden on healthcare resources and enhances patient convenience.
Despite its many benefits, dabigatran etexilate is not without limitations. Renal function plays a crucial role in its metabolism and elimination, necessitating dose adjustments in patients with impaired renal function. Additionally, there is a risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects, such as dyspepsia and gastritis, although these are generally mild and transient.
Future Directions and Challenges
Looking ahead, ongoing research aims to further refine the use of dabigatran etexilate and explore its potential in additional clinical scenarios. Pharmacogenomic studies may help identify genetic factors influencing drug response, allowing for personalized dosing strategies. Additionally, comparative effectiveness studies may provide insights into the optimal positioning of dabigatran etexilate relative to other direct oral anticoagulants.

In conclusion, dabigatran etexilate represents a significant advancement in oral anticoagulant therapy, offering efficacy, safety, and convenience in the management of thrombotic disorders. The development of pellets as a formulation option further enhances its therapeutic potential, paving the way for individualized treatment approaches and improved patient outcomes. As our understanding of this agent continues to evolve, dabigatran etexilate is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of anticoagulation therapy.