Comparative Analysis of Abemaciclib and Other CDK4/6 Inhibitors
CDK4/6 inhibitors have become a vital weapon in the fight against breast cancer. This article delves into their function, explores abemaciclib API, a prominent CDK4/6 inhibitor, and compares it to its counterparts.
Whats is CDK4/6 Inhibitors?
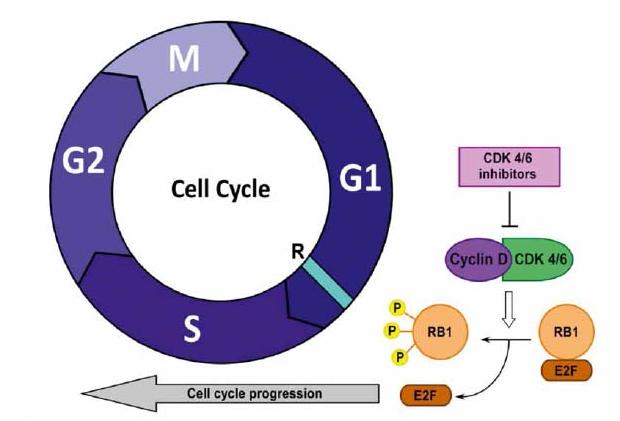
Cell division is a tightly regulated process overseen by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) play a pivotal role in this process, functioning as key regulatory proteins at the G1/S phase transition – a critical checkpoint where a cell prepares to replicate its DNA before mitosis. CDK4/6 activity is contingent upon binding with specific cyclin partners. This coordinated action triggers phosphorylation events that initiate DNA replication, propelling the cell forward into the S phase.
CDK4/6 inhibitors represent a class of targeted therapeutic agents designed to disrupt this essential cell cycle regulatory pathway. These drugs act as competitive inhibitors, mimicking the structure of cyclins and binding to CDK4/6 with high affinity. By effectively sequestering CDK4/6, they prevent the formation of functional CDK4/6-cyclin complexes. This renders the CDK4/6 signaling cascade inoperable, thereby halting cell cycle progression.
The Downstream Effect on Cancer Cells
The dysregulation of cell cycle control is a hallmark of cancer. In hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, aberrant signaling pathways often lead to the constitutive activation of CDK4/6, promoting uncontrolled cell proliferation. CDK4/6 inhibitors effectively target this vulnerability.
By inhibiting CDK4/6 activity, these drugs can exert multiple anti-tumor effects:
- Cell Cycle Arrest: Disruption of CDK4/6 signaling prevents the phosphorylation events necessary for DNA replication, effectively stalling cancer cells at the G1/S checkpoint and impeding their progression through the cell cycle.
- Proliferation Inhibition: The inability to complete DNA replication hinders cancer cell proliferation, leading to a decline in the tumor cell population.
- Potential for Cell Death: In some instances, CDK4/6 inhibition can trigger apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells.
It is noteworthy that CDK4/6 inhibitors are often employed synergistically with other therapeutic modalities, such as hormonal therapy. This combinatorial approach capitalizes on the complementary mechanisms of action of each treatment, maximizing therapeutic efficacy in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.
What is Abemaciclib API?
Abemaciclib isn’t just a brand name medication; it’s also known as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). Think of an API as the key component that gives a drug its specific effect.
- Pure Substance: An API is a highly purified substance with a defined chemical structure. This ensures consistent quality and predictable effects within the medication.
- Dosage Form: Abemaciclib itself wouldn’t be directly administered to a patient. Instead, it’s combined with inactive ingredients like fillers, binders, and disintegrants. This creates a stable and deliverable dosage form, such as capsules or tablets.
- Manufacturing: Pharmaceutical companies obtain abemaciclib API from manufacturer who specialize in producing high-grade ingredients for medications. Strict regulations govern the manufacturing process to ensure the API’s purity and safety.
- Clinical Trials: Abemaciclib API goes through extensive testing before becoming part of an approved medication. This ensures the drug’s safety and efficacy when administered in the final dosage form.
By understanding the role of the API, we can appreciate the foundation upon which medications like abemaciclib are built.
Comparative Analysis of CDK4/6 Inhibitors
Abemaciclib vs. Palbociclib
Palbociclib, the first FDA-approved CDK4/6 inhibitor, operates by inhibiting CDK4/6 to halt cell cycle progression.
| Aspect | Abemaciclib | Palbociclib |
| Efficacy | Demonstrated prolonged PFS in MONARCH trials | Significantly prolonged PFS in PALOMA trials |
| (MONARCH-2, MONARCH-3) | (PALOMA-2, PALOMA-3) | |
| Safety Profile | Common side effect: diarrhea | Common side effect: neutropenia |
| Managed with antidiarrheal agents | Managed with dose interruptions | |
| Dosing Schedule | Continuous dosing regimen | 3 weeks on, 1 week off |
| Clinical Trials | MONARCH-2, MONARCH-3 | PALOMA-2, PALOMA-3 |
| FDA Approval | Approved in 2017 | Approved in 2015 |
Abemaciclib vs. Ribociclib
Ribociclib, another FDA-approved CDK4/6 inhibitor, operates by inhibiting CDK4/6 to halt cell cycle progression.
| Aspect | Abemaciclib | Ribociclib |
| Efficacy | Demonstrated comparable PFS in MONARCH trials | Demonstrated comparable PFS in MONALEESA trials |
| (MONARCH-3, MONARCH-7) | (MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-7) | |
| Safety Profile | Common side effect: diarrhea | Common side effect: neutropenia |
| Managed with antidiarrheal agents | Managed with dose interruptions | |
| Dosing Schedule | Continuous dosing regimen | 3 weeks on, 1 week off |
| Clinical Trials | MONARCH-3, MONARCH-7 | MONALEESA-2, MONALEESA-7 |
| FDA Approval | Approved in 2017 | Approved in 2017 |
Real-World Data and Practical Considerations
- Patient Selection: Factors influencing treatment selection include patient age, comorbidities, and treatment history.
- Cost and Accessibility: Differences in cost and insurance coverage may influence therapeutic choices.
- Ongoing Research: Continued research and clinical trials are pivotal in refining therapeutic strategies and optimizing outcomes.
The comparative analysis of Abemaciclib with other CDK4/6 inhibitors, Palbociclib and Ribociclib, highlights nuanced differences in efficacy, safety profiles, and dosing schedules. These distinctions underscore the importance of personalized treatment strategies in optimizing outcomes for patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer and other malignancies. Continued research efforts and real-world data will further refine our understanding and application of CDK4/6 inhibitors in clinical practice.
Recent Developments
The field of CDK4/6 inhibitors is constantly evolving, with new research and clinical trials aiming to improve their effectiveness and explore their application in various cancers. Here’s a detailed breakdown for the Recent Developments section of your comparative analysis:
1. Expanding Use in Early-Stage Cancers:
Briefly mention the ongoing exploration of using CDK4/6 inhibitors, particularly Abemaciclib, in the adjuvant setting (following surgery or primary treatment) for high-risk early-stage breast cancer. Mention trials like MonarchE [clinical trials on MonarchE can be found online] investigating this approach.
2. Treatment After Progression on Prior CDK4/6 Inhibitors:
Highlight the recent findings from the postMONARCH trial (June 2024, ASCO) suggesting Abemaciclib combined with fulvestrant might be beneficial for patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who progressed on a different CDK4/6 inhibitor.
Briefly mention real-world data suggesting Abemaciclib after progression might extend progression-free survival, but emphasize the need for further confirmation from ongoing trials.
3. Combination Therapies with Immunotherapy:
Discuss the ongoing research on combining CDK4/6 inhibitors with immunotherapy drugs like pembrolizumab or nivolumab. Mention trials like NEWFLAME that explored the combination of Abemaciclib, nivolumab, and endocrine therapy but resulted in high immune-related side effects. Emphasize the need for further research to optimize combination strategies.
4. Targeting Specific Mutations:
Briefly mention the development of next-generation CDK4/6 inhibitors that target specific mutations or have different selectivity profiles compared to current options. This is an active area of research with the potential for personalized treatment approaches.
Abemaciclib Cost
The cost of abemaciclib is a crucial consideration for patients and healthcare providers. As of recent data, the average wholesale price for a 30-day supply of Abemaciclib can range from $12,000 to $13,000. This high cost can be attributed to the complexities involved in drug development, clinical trials, and the production of high-quality pharmaceuticals. Insurance coverage and patient assistance programs play vital roles in making this medication accessible. Patients should consult with their healthcare providers and insurance companies to understand their coverage options and potential out-of-pocket costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Abemaciclib stands out in cancer therapy due to its potent CDK4/6 inhibition and monotherapy use. Its unique pharmacological profile differentiates it from Palbociclib and Ribociclib. Ongoing research continues to explore its full potential, promising better outcomes for patients.