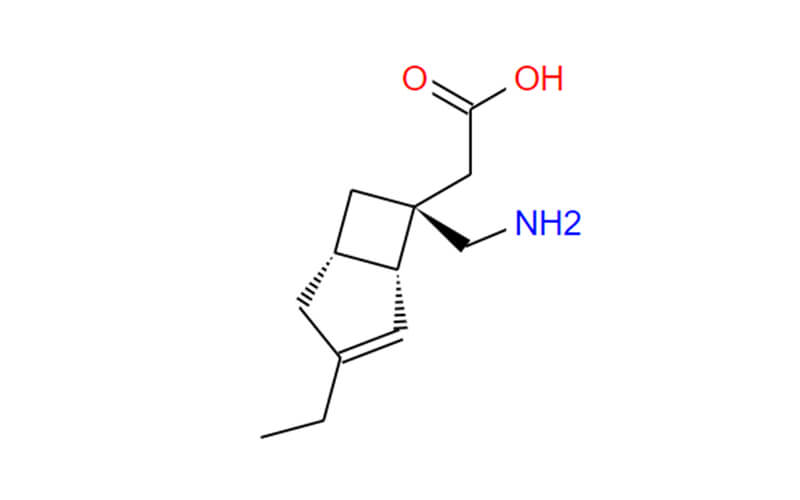
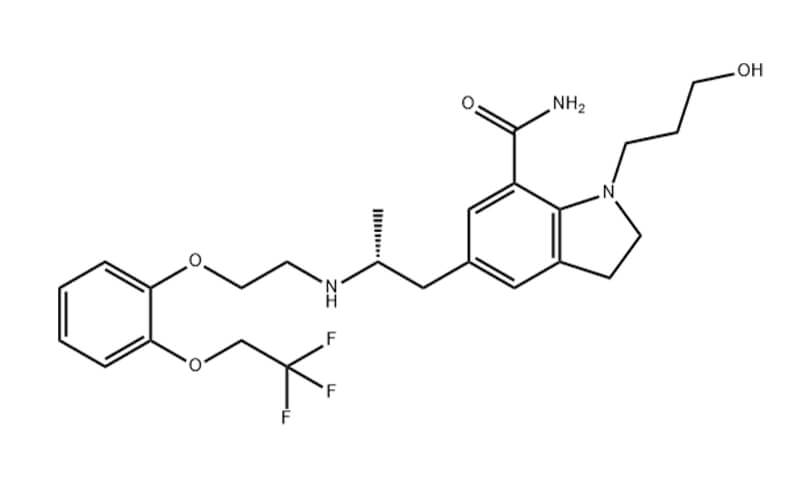
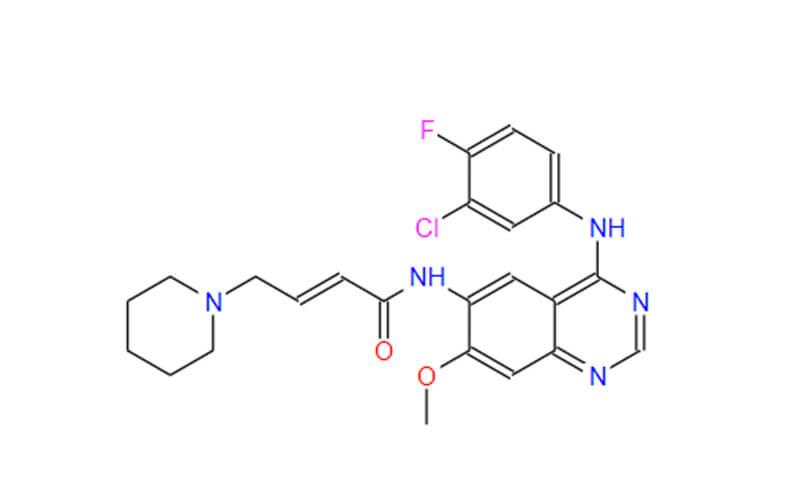
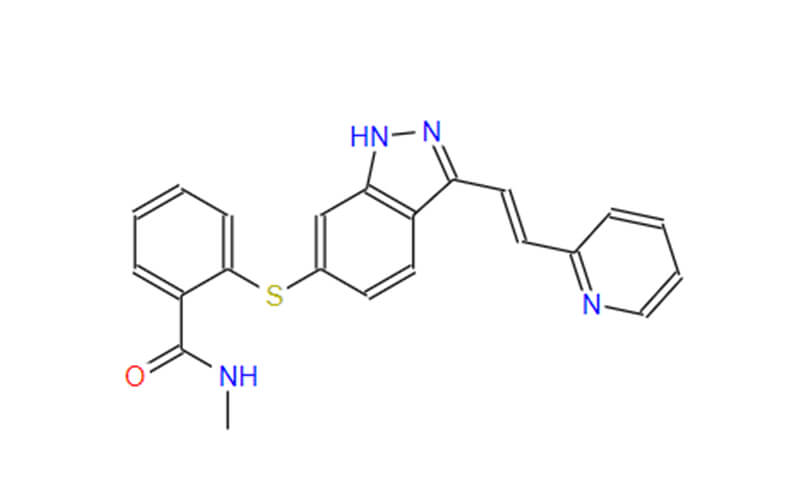
An Overview of Pharmaceutical Intermediates: What You Should Know?
The pharmaceutical industry is a complex and ever-evolving landscape, with a constant stream of new drugs and therapies emerging to address various medical needs. Behind the scenes of this intricate world lies a crucial component: pharmaceutical intermediates. These intermediate compounds play a pivotal role in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), the essential components that impart therapeutic effects in medications.
The Significance of Intermediates in Pharma Industry
Pharmaceutical intermediates are organic compounds that serve as precursors in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). APIs, the heart of any pharmaceutical product, are the active substances responsible for producing the desired therapeutic effect in the body.
Intermediates bridge the gap between the starting materials, often simple chemicals, and the complex APIs. They undergo a series of chemical transformations, each meticulously designed to introduce the desired functional groups and molecular structures.
The significance of intermediates in the pharma industry is multifaceted:
- Efficiency: Intermediates allow for the efficient production of APIs by breaking down the complex synthesis process into manageable steps.
- Quality Control: The synthesis of intermediates provides multiple checkpoints for quality control, ensuring the purity and consistency of the final API.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Intermediates can be synthesized in bulk, reducing production costs and improving overall cost-effectiveness.
Intellectual Property Protection: The synthesis of intermediates can be patented, protecting intellectual property and preventing unauthorized production of APIs.
Key Types of Pharmaceutical Intermediates
There are many different types of pharmaceutical intermediates, but some of the most common include:
- Starting materials: These are the simplest organic compounds that are used as the initial building blocks for API synthesis. They are typically readily available from commercial sources or derived from natural sources.
- Key intermediates: These intermediates represent significant milestones in the API synthesis process, as they possess structural features closely resembling the final API. Their synthesis often involves multi-step reactions and careful optimization to ensure high purity and yield.
- Chiral intermediates: Chiral intermediates contain stereocenters, which means they exist in two mirror-image forms (enantiomers). The stereochemistry of these intermediates is crucial for the biological activity of the final API, as different enantiomers can have distinct pharmacological effects.
- Pro-drugs: Pro-drugs are inactive forms of the API that undergo enzymatic conversion within the body to release the active drug molecule. They are designed to improve the absorption, stability, or targeting of the API.
- Peptide intermediates: Peptide intermediates are derived from amino acids and are used to synthesize peptide-based drugs, such as hormones, enzymes, and antimicrobials. Their synthesis requires precise control of reaction conditions to ensure the correct sequence and stereochemistry of amino acids.
- Biotechnological intermediates: Biotechnological intermediates are produced using biological processes, such as fermentation or cell culture. They are often complex molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, or oligonucleotides, used in biopharmaceutical drugs.

Challenges in Pharmaceutical Intermediate Synthesis
The synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates is a complex and demanding undertaking, requiring a deep understanding of organic chemistry, reaction conditions, and purification techniques. Key challenges include:
- Selectivity: Ensuring that the desired chemical reactions occur selectively, minimizing unwanted side reactions and impurities.
- Yield: Maximizing the amount of desired product obtained from the starting materials to ensure cost-effectiveness.
- Purity: Achieving high purity levels to meet stringent regulatory standards and ensure the safety and efficacy of the final API.
- Scalability: Developing synthetic processes that can be scaled up from small-scale laboratory experiments to large-scale commercial production.
- Cost-effectiveness: Optimizing synthetic routes to minimize production costs and ensure commercial viability.
- Environmental Considerations: Employing environmentally friendly synthetic methods to minimize hazardous waste generation and environmental impact.

Qingmu Pharmaceutical: A Trusted Pharma Intermediates Manufacturer
Qingmu Pharmaceutical is a leading manufacturer of pharmaceutical intermediates with a strong track record of quality and innovation. The company offers a wide range of intermediates for the synthesis of APIs used in various therapeutic areas, including:
- Antibiotics: Intermediates for the synthesis of penicillin, cephalosporins, and other antibiotics.
- Anticancer drugs: Intermediates for the synthesis of cytotoxic agents, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies.
- Cardiovascular drugs: Intermediates for the synthesis of antihypertensives, antianginals, and cholesterol-lowering agents.
Qingmu Pharmaceutical is committed to providing high-quality intermediates that meet the stringent requirements of the pharmaceutical industry. The company has a team of experienced scientists and engineers dedicated to developing and manufacturing innovative intermediates for the production of life-saving medications.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical intermediates play a vital role in the development and production of safe and effective medications. Their significance extends beyond their structural contribution, encompassing efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety. Qingmu Pharmaceutical stands as a trusted partner in the pharmaceutical industry, providing high-quality intermediates that contribute to the advancement of healthcare.