Advancements in Treating Neuropathic Pain: The Clinical Evolution of Mirogabalin as a Unique Selective Gabapentinoid
Chronic pain, a debilitating condition affecting millions worldwide, presents a significant challenge for both patients and healthcare professionals. Among the various types of chronic pain, neuropathic pain, characterized by nerve damage and abnormal pain signaling, poses a particularly complex treatment dilemma. Fortunately, recent advancements in research have led to the exploration of novel therapeutic options, offering hope for improved pain management. In this context, mirogabalin, a novel selective gabapentinoid, has emerged as a promising contender in the fight against neuropathic pain.
Getting to Know the Background of Mirogabalin
Mirogabalin, a recent addition to the fight against neuropathic pain, stands out as a unique selective gabapentinoid with promising clinical potential. To fully comprehend its significance, we need to delve deeper into its background, exploring its chemical nature, mechanism of action, and the rationale behind its development.
1. Chemical Classification:
Mirogabalin belongs to the class of alpha-2-delta (α2δ) ligand drugs. These drugs bind to specific subunits (α2δ) of voltage-gated calcium channels, which play a crucial role in nerve signaling and pain transmission.
2. Mechanism of Action:
Unlike traditional gabapentinoids like gabapentin and pregabalin, which have a broader mechanism of action, mirogabalin exhibits selectivity. It primarily binds to the α2δ-1 and α2δ-2 subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels, specifically targeting these particular sites involved in pain signaling pathways. This targeted interaction is believed to be responsible for its potential benefits:
- Reduced Side Effects: By focusing on specific subunits, mirogabalin potentially avoids interaction with other areas of the nervous system, leading to a lower risk of side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, and cognitive impairment, which are commonly observed with broader-acting gabapentinoids.
- Potential for Improved Efficacy: Selective targeting of pain-related pathways might lead to enhanced pain-relieving effects compared to medications with a broader mechanism of action.
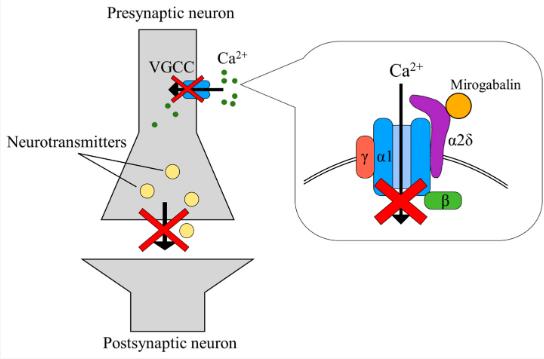
3. Rationale for Development:
The development of mirogabalin stemmed from the need for more targeted and potentially safer options for managing neuropathic pain. Traditional gabapentinoids, while effective, often come with limitations like dose-dependent side effects and potential for cognitive impairment.
Researchers aimed to create a new generation of gabapentinoids with improved selectivity and a better side effect profile. Extensive research led to the discovery of mirogabalin, which demonstrated promising preclinical and clinical results, suggesting its potential as a valuable addition to the treatment landscape for neuropathic pain.
It is important to remember that mirogabalin is still relatively new in the market, and further research is ongoing to fully establish its long-term safety and efficacy compared to existing medications.
Clinical Trials of Mirogabalin
The clinical journey of mirogabalin has been marked by comprehensive and rigorous testing through various clinical trials. To understand its potential and limitations better, let’s delve deeper into the details of these trials:
1. Phase 1 Trials:
These initial trials primarily focused on evaluating the safety and tolerability of mirogabalin in healthy volunteers. They explored different dosage ranges and administration schedules to determine the optimal therapeutic window while identifying any potential side effects.
2. Phase 2 Trials:
Building on the safety data from Phase 1, Phase 2 trials involved a larger number of patients with diagnosed neuropathic pain. These trials primarily aimed to assess the efficacy of mirogabalin in reducing pain and improving other related symptoms like sleep disturbances and sensory abnormalities. Different dosages were compared against a placebo to determine the most effective and well-tolerated dose regimen.
3. Phase 3 Trials:
These large-scale, pivotal trials play a crucial role in establishing the safety and efficacy of a drug for potential market approval. In the case of mirogabalin, several Phase 3 trials were conducted specifically for:
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP): These trials involved adult patients with confirmed DPNP. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either different doses of mirogabalin, a placebo, or an existing treatment for DPNP. The primary endpoint of these trials was the change in average daily pain scores, measured using validated pain scales. Secondary endpoints included other pain-related measures, such as sleep quality and functional limitations.
- Post-Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN): Similar to the DPNP trials, these studies involved adult patients with confirmed PHN. They compared the efficacy and safety of mirogabalin against a placebo using similar outcome measures, focusing primarily on pain reduction and improvement in daily functioning.

Key Findings from Clinical Trials
Across the various clinical trials, mirogabalin demonstrated several promising findings:
- Significant Pain Reduction: Compared to placebo, mirogabalin treatment resulted in statistically significant reductions in average daily pain scores in both DPNP and PHN patients.
- Improved Functioning: Participants receiving mirogabalin reported improvements in sleep quality, reduced interference of pain with daily activities, and overall functional capacity.
- Favorable Safety Profile: The incidence of side effects was generally lower with mirogabalin compared to other gabapentinoids, potentially due to its selective mechanism of action.
- Dose-Dependent Response: Studies observed a dose-dependent effect, with higher doses leading to greater pain relief. However, the optimal dosage balance between efficacy and tolerability needs further evaluation.
Limitations and Ongoing Research
While the clinical trial data is encouraging, it is essential to acknowledge certain limitations:
- Limited Long-Term Data: Most trials had a duration of 12 weeks, and long-term data regarding safety and efficacy beyond this timeframe is still limited.
- Geographic Focus: The majority of Phase 3 trials were conducted in Asian populations, and further studies are needed to confirm efficacy and safety in diverse populations globally.
- Head-to-Head Comparisons: While comparisons with placebo were conducted, direct comparisons with other existing gabapentinoids in the same trials are limited.
Despite these limitations, ongoing research is addressing these gaps. Additional trials are underway to:
- Evaluate long-term safety and efficacy of mirogabalin.
- Investigate its effectiveness in other types of neuropathic pain.
- Explore its potential in combination therapy with other pain medications.
- Conduct head-to-head comparisons with other gabapentinoids to establish its relative advantages and limitations.
The clinical trial data on mirogabalin provides a strong foundation for its potential as a valuable treatment option for neuropathic pain. By addressing the existing limitations and continuing research efforts, scientists and healthcare professionals can further elucidate the role of this novel gabapentinoid in improving the lives of individuals struggling with chronic pain.
Comparison of Mirogabalin with Existing Gabapentinoids
While both traditional gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) and mirogabalin share the same classification, their mechanisms of action and potential advantages differ significantly. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Mechanism of Action
- Traditional Gabapentinoids: Gabapentin and pregabalin work through a less understood mechanism. They are believed to bind to multiple voltage-gated calcium channels throughout the nervous system, not just those specifically involved in pain signaling. This broader interaction can lead to side effects in areas unrelated to pain management.
- Mirogabalin: Unlike its counterparts, mirogabalin exhibits greater selectivity. It primarily targets the alpha-2-delta subunits (α2δ) of voltage-gated calcium channels, particularly the α2δ-1 subunit, which plays a crucial role in pain signaling pathways. This targeted interaction minimizes the medication’s influence on other systems, potentially reducing the risk of certain side effects.
2. Dosage and Side Effects
- Traditional Gabapentinoids: These medications often require higher dosages to achieve therapeutic effects, which can contribute to a higher incidence of side effects like drowsiness, dizziness, and cognitive impairment.
- Mirogabalin: Studies suggest that mirogabalin might be equally effective at lower doses compared to other gabapentinoids. This potentially reduces the overall side effect burden, making it a potentially more tolerable option for some patients.
3. Onset of Action
- Traditional Gabapentinoids: The onset of action for traditional gabapentinoids can be slower, meaning it may take longer for patients to feel pain relief.
- Mirogabalin: Some clinical trials indicate that mirogabalin may have a faster onset of action compared to other gabapentinoids. This can be particularly beneficial for patients seeking quicker pain relief.
Current Status and Future Directions
Mirogabalin has received regulatory approval in Japan for the treatment of both diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain (DPNP) and post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). This marks a significant milestone in its clinical journey, offering a novel treatment option for patients suffering from these debilitating conditions in this region.
However, its availability extends beyond Japan. Mirogabalin is currently undergoing evaluation for potential registration in other countries, including the United States and Europe. This involves navigating the regulatory processes of each jurisdiction, conducting additional clinical trials if necessary, and accumulating further data to support its safety and efficacy. The specific timelines for registration and approval in each region will depend on the individual regulatory requirements and ongoing evaluations.

Mirogabalin API Manufacturer: Qingmu Pharmaceutical
Sichuan Qingmu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., often simply referred to as Qingmu Pharmaceutical, is a leading manufacturer of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) based in Sichuan, China. The company specializes in the development, production, and distribution of high-quality APIs for various therapeutic applications, including neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and oncology.
Mirogabalin is one of the key products manufactured by Qingmu. Qingmu Pharmaceutical operates state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities that adhere to strict quality standards and regulatory requirements. The company employs advanced technologies and processes to ensure the purity, potency, and consistency of its APIs. With a focus on research and development, Qingmu Pharmaceutical continuously strives to enhance its manufacturing capabilities and expand its product portfolio to address unmet medical needs.
This Mirogabalin supplier places a strong emphasis on quality assurance throughout the manufacturing process. The company implements stringent quality control measures at every stage, from raw material procurement to final product testing. By adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other international quality standards, Qingmu ensures the safety, efficacy, and reliability of its APIs.
In addition to its dedication to product quality and innovation, Qingmu is committed to environmental sustainability and corporate social responsibility. The company prioritizes eco-friendly practices and invests in initiatives to minimize its environmental footprint. By promoting sustainable development and responsible business practices, Qingmu Pharmaceutical aims to make a positive impact on both society and the environment.